
Knocking (also knock, detonation, spark knock, pinging or pinking) in spark-ignition internal combustion engines occurs when combustion of the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder does not start off correctly in response to ignition by the spark plug, but one or more pockets of air/fuel mixture explode outside the envelope of the normal combustion front.
The fuel-air charge is meant to be ignited by the spark plug only, and at a precise point in the piston's stroke. Knock occurs when the peak of the combustion process no longer occurs at the optimum moment for the four-stroke cycle. The shock wave creates the characteristic metallic "pinging" sound, and cylinder pressure increases dramatically. Effects of engine knocking range from inconsequential to completely destructive.
Knocking should not be confused with – they are two separate events. However, pre-ignition is usually followed by knocking.
Normal combustion[edit]
Under ideal conditions the common internal combustion engine burns the fuel/air mixture in the cylinder in an orderly and controlled fashion. The combustion is started by the spark plug some 10 to 40 crankshaft degrees prior to top dead center (TDC), depending on many factors including engine speed and load. This ignition advance allows time for the combustion process to develop peak pressure at the ideal time for maximum recovery of work from the expanding gases.
In the case of highly supercharged or high compression multi-cylinder engines particularly ones that use methanol (or other fuels prone to pre-ignition) pre-ignition can quickly melt or burn pistons since the power generated by other still functioning pistons will force the overheated ones along no matter how early the mix pre-ignites. Many engines have suffered such failure where improper fuel delivery is present. Often one injector may clog while the others carry on normally allowing mild detonation in one cylinder that leads to serious detonation, then pre-ignition.
The challenges associated with pre-ignition have increased in recent years with the development of highly boosted and "downspeeded" spark ignition engines. The reduced engine speeds allow more time for autoignition chemistry to complete thus promoting the possibility of pre-ignition and so called "mega-knock". Under these circumstances, there is still significant debate as to the sources of the pre-ignition event.
Pre-ignition and engine knock both sharply increase combustion chamber temperatures. Consequently, either effect increases the likelihood of the other effect occurring, and both can produce similar effects from the operator's perspective, such as rough engine operation or loss of performance due to operational intervention by a powertrain-management computer. For reasons like these, a person not familiarized with the distinction might describe one by the name of the other. Given proper combustion chamber design, pre-ignition can generally be eliminated by proper spark plug selection, proper fuel/air mixture adjustment, and periodic cleaning of the combustion chambers.
RELATED VIDEO



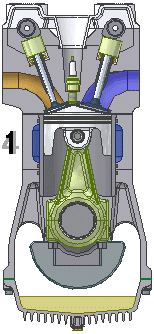 An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert energy into useful mechanical motion. Heat engines, including internal combustion engines and external combustion engines (such as steam engines) burn a fuel to create heat which is then used to create motion...
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert energy into useful mechanical motion. Heat engines, including internal combustion engines and external combustion engines (such as steam engines) burn a fuel to create heat which is then used to create motion...
 A Stirling engine is a heat engine operating by cyclic compression and expansion of air or other gas, the working fluid, at different temperature levels such that there is a net conversion of heat energy to mechanical work.
A Stirling engine is a heat engine operating by cyclic compression and expansion of air or other gas, the working fluid, at different temperature levels such that there is a net conversion of heat energy to mechanical work.







