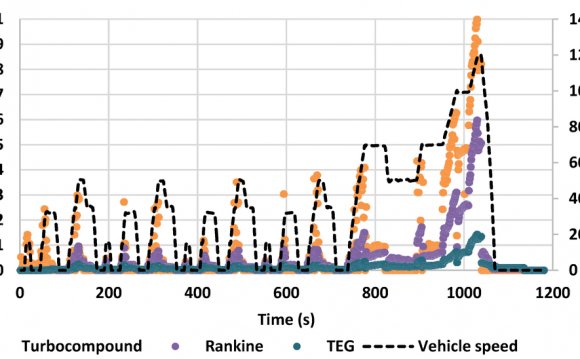
 The cycle variation characteristics of a port fuel injection hydrogen internal combustion engine (PFI-HICE) have been extensively investigated. The covariance of indicated mean effective pressure (COVimep) is the best parameter for evaluating the cycle variations in the PFI-HICE. COVimep decreases as fuel–air ratio increases from 1000 to 5500 rpm, and engine speed minimally affects COVimep. The effect of ignition advance angle on COVimep is determined by fuel–air ratio. The ignition advance angles that correspond to the minimum COVimep of the PFI-HICE decrease as fuel–air ratio increases. The effect of ignition advance angle on COVimep diminishes as fuel–air ratio increases. The COVimep of the PFI-HICE rapidly decreases as throttle increases when the throttle is less than 20%. Injection timing only slightly affects COVimep under high-speed conditions, and COVimep increases when hydrogen is injected in intake periods under low-speed conditions. These results indicate that studying COVimep improves the stability of PFI-HICEs.
The cycle variation characteristics of a port fuel injection hydrogen internal combustion engine (PFI-HICE) have been extensively investigated. The covariance of indicated mean effective pressure (COVimep) is the best parameter for evaluating the cycle variations in the PFI-HICE. COVimep decreases as fuel–air ratio increases from 1000 to 5500 rpm, and engine speed minimally affects COVimep. The effect of ignition advance angle on COVimep is determined by fuel–air ratio. The ignition advance angles that correspond to the minimum COVimep of the PFI-HICE decrease as fuel–air ratio increases. The effect of ignition advance angle on COVimep diminishes as fuel–air ratio increases. The COVimep of the PFI-HICE rapidly decreases as throttle increases when the throttle is less than 20%. Injection timing only slightly affects COVimep under high-speed conditions, and COVimep increases when hydrogen is injected in intake periods under low-speed conditions. These results indicate that studying COVimep improves the stability of PFI-HICEs.
Highlights
► The COVimep of hydrogen fueled engine decreases as fuel–air ratio increases. ► Fuel–air ratio has a more remarkable effect on COVimep than ignition advance angle. ► COVimep exhibits no remarkable change with larger throttle positions. ► At idle conditions, the hydrogen injection process strongly affects COVimep.
Keywords
- Hydrogen;
- Hydrogen internal combustion engine;
- Cycle variation
RELATED VIDEO



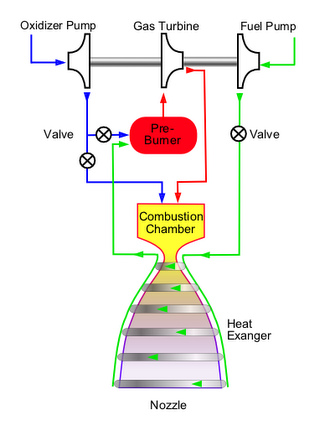 The staged combustion cycle, also called topping cycle or pre-burner cycle, is a thermodynamic cycle of bipropellant rocket engines. Some of the propellant is burned in a pre-burner and the resulting hot gas is used to power the engine's turbines and pumps. The...
The staged combustion cycle, also called topping cycle or pre-burner cycle, is a thermodynamic cycle of bipropellant rocket engines. Some of the propellant is burned in a pre-burner and the resulting hot gas is used to power the engine's turbines and pumps. The...
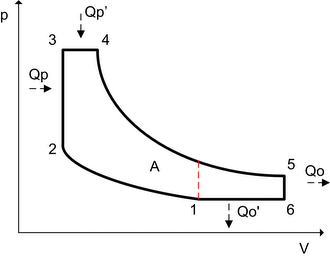 The Atkinson cycle engine is a type of internal combustion engine invented by James Atkinson in 1882. The Atkinson cycle is designed to provide efficiency at the expense of power density, and is used in some modern hybrid electric applications.
The Atkinson cycle engine is a type of internal combustion engine invented by James Atkinson in 1882. The Atkinson cycle is designed to provide efficiency at the expense of power density, and is used in some modern hybrid electric applications.







