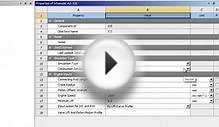
First, you will need to supply a few parameters. You need to enter in the "Brake Mean Effective Cylinder Pressure", which is in units of pounds per square inch. Typical values for a OEM 4-stroke engine are 125 to 150 lbs/in2, and for turbocharged engines the values range from 180 to 250 lbs/in2. You also need to enter in the peak torque value in foot-pounds. You also select if you are designing a 2 or 4-stroke engine, and the number of cylinders. The last thing to enter is the ratio of connecting rod length to cylinder bore - for example a value of 2.0 means that the connecting rod length will be twice the cylinder bore size. A value somewhere around 0.8 to 1.2 works well.
The program will determine values for the displacement of the engine (in cubic-inches), the cylinder bore size (inches), connecting rod length (inches), the maximum engine RPM (this assumes a maximum piston speed of 15 meters/sec), and the engine horsepower. All this from a few input parameters - amazing!
RELATED VIDEO